Until a pair of years in the past, Lucy Calkins was, to many American academics and oldsters, a minor deity. 1000’s of U.S. colleges used her curriculum, known as Items of Research, to show youngsters to learn and write. 20 years in the past, her guiding ideas—that youngsters be taught finest once they love studying, and that academics ought to attempt to encourage that love—turned a centerpiece of the curriculum in New York Metropolis’s public colleges. Her strategy unfold by an institute she based at Columbia College’s Academics School, and traveled additional nonetheless by way of instructing supplies from her writer. Many academics don’t consult with Items of Research by title. They merely say they’re “instructing Lucy.”
However now, on the age of 72, Calkins faces the destruction of every part she has labored for. A 2020 report by a nonprofit described Items of Research as “superbly crafted” however “unlikely to result in literacy success for all of America’s public schoolchildren.” The criticism turned unattainable to disregard two years later, when the American Public Media podcast Offered a Story: How Instructing Children to Learn Went So Incorrect accused Calkins of being one of many causes so many American youngsters battle to learn. (The Nationwide Evaluation of Academic Progress—a take a look at administered by the Division of Schooling—present in 2022 that roughly one-third of fourth and eighth graders are unable to learn on the “fundamental” degree for his or her age.)
In Offered a Story, the reporter Emily Hanford argued that academics had fallen for a single, unscientific concept—and that its persistence was holding again American literacy. The concept was that “starting readers don’t must sound out phrases.” That meant academics had been not encouraging early learners to make use of phonics to decode a brand new phrase—to say cuh–ah–tuh for “cat,” and so forth. As an alternative, youngsters had been anticipated to determine the phrase from the primary letter, context clues, or close by illustrations. However this “cueing” system was not working for big numbers of youngsters, leaving them floundering and annoyed. The end result was a studying disaster in America.
The podcast stated that “an organization and 4 of its prime authors” had bought this “incorrect concept” to academics and politicians. The corporate was the academic writer Heinemann, and the authors included the New Zealander Marie Clay, the American duo Irene Fountas and Homosexual Su Pinnell, and Calkins. The podcast devoted a complete episode, “The Famous person,” to Calkins. In it, Hanford questioned if Calkins was wedded to a “romantic” notion of literacy, the place youngsters would fall in love with books and would then someway, magically, be taught to learn. Calkins couldn’t see that her system failed poorer youngsters, Hanford argued, as a result of she was “influenced by privilege”; she had written, for example, that youngsters may be taught in regards to the alphabet by selecting out letters from their environment, akin to “the monogram letters on their bathtub towels.”
In Hanford’s view, it was no shock if Calkins’s technique labored high-quality for wealthier youngsters, lots of whom arrive in school already beginning to learn. In the event that they struggled, they may at all times flip to non-public tutors, who may give the phonics classes that their colleges had been neglecting to offer. However youngsters with out entry to non-public tutors wanted to be drilled in phonics, Hanford argued. She backed up her claims by referencing neurological analysis into how youngsters be taught to learn—gesturing to a physique of proof often known as “the science of studying.” That analysis demonstrated the significance of standard, specific phonics instruction, she stated, and ran opposite to how American studying academics had been being skilled.
Because the podcast aired, “instructing Lucy” has fallen out of trend. Calkins’s critics say that her refusal to acknowledge the significance of phonics has tainted not simply Items of Research—a studying and writing program that stretches as much as eighth grade—however her complete academic philosophy, often known as “balanced literacy.” Forty states and the District of Columbia have handed legal guidelines or carried out insurance policies selling the science of studying prior to now decade, in response to Schooling Week, and publishers are racing to regulate their choices to embrace that philosophy.
Someway, the broader debate over how one can educate studying has grow to be a referendum on Calkins herself. In September 2023, Academics School introduced that it could dissolve the reading-and-writing-education heart that she had based there. Anti-Lucy sentiment has proliferated, notably within the metropolis that when championed her strategies: Final 12 months, David Banks, then the chancellor of New York Metropolis public colleges, likened educators who used balanced literacy to lemmings: “All of us march proper off the aspect of the mountain,” he stated. The New Yorker has described Calkins’s strategy as “literacy by vibes,” and in an editorial, the New York Publish described her initiative as “a catastrophe” that had been “imposed on generations of American youngsters.” The headline declared that it had “Ruined Numerous Lives.” When the celebrated Harvard cognitive psychologist Steven Pinker shared an article about Calkins on X, he bemoaned “the scandal of ed colleges that promote studying quackery.” Queen Lucy has been dethroned.
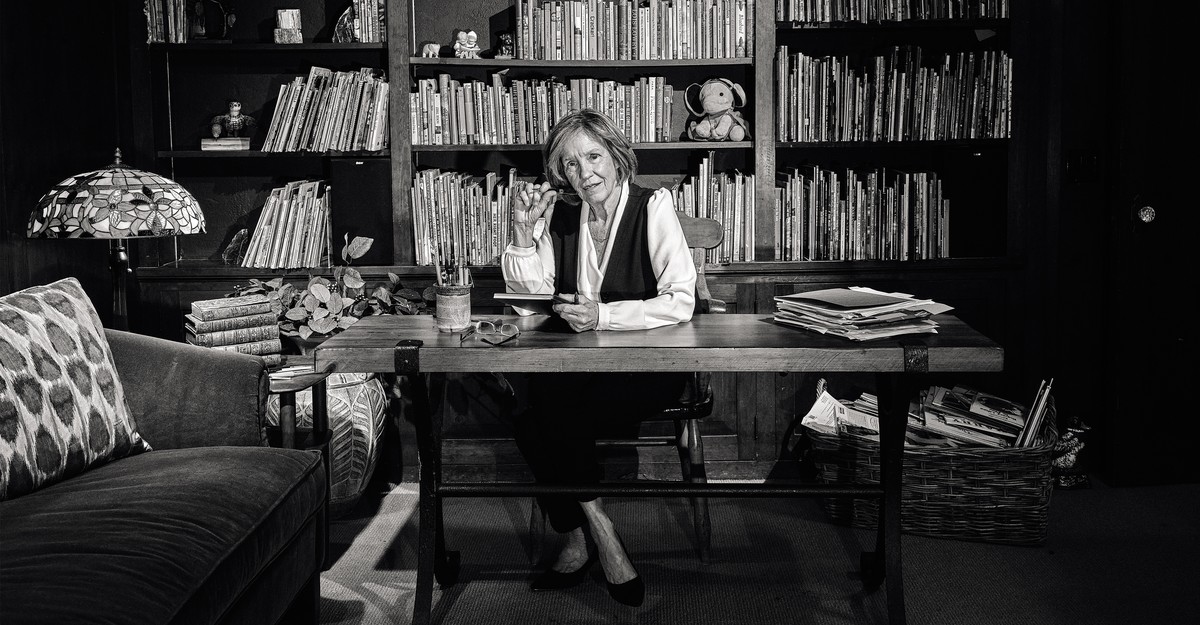
“I imply, I can say it—it was a little bit bit like 9/11,” Calkins instructed me once we spoke at her dwelling this summer time. On that day in 2001, she had been driving into New York Metropolis, and “actually, I used to be on the West Aspect Freeway and I noticed the aircraft crash into the tower. Your thoughts can’t even comprehend what’s occurring.” 20 years later, the suggestion that she had harmed youngsters’s studying felt like the identical sort of intestine punch.
Calkins now concedes that among the issues recognized in Offered a Story had been actual. However she says that she had adopted the analysis, and was making an attempt to rectify points even earlier than the podcast debuted: She launched her first devoted phonics items in 2018, and later revealed a sequence of “decodable books”—simplified tales that college students can simply sound out. Nonetheless, she has not managed to fulfill her critics, and on the third day we spent collectively, she admitted to feeling despondent. “What surprises me is that I really feel as if I’ve performed all of it,” she instructed me. (Heinemann, Calkins’s writer, has claimed that the Offered a Story podcast “radically oversimplifies and misrepresents complicated literacy points.”)
The backlash towards Calkins strikes some onlookers, even those that should not paid-up Lucy partisans, as unfair. “She wouldn’t have been my alternative for the image on the ‘needed’ poster,” James Cunningham, a professor emeritus of literacy research on the College of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, instructed me. Certainly, over the course of a number of days spent with Calkins, and plenty of extra hours speaking with individuals on all sides of this debate, I got here to see her downfall as half of a bigger story in regards to the competing currents in American training and the common need for a straightforward, off-the-shelf resolution to the nation’s studying issues.
The query now’s whether or not Calkins is a lot part of the issue that she can’t be a part of the answer. “I’m going to determine this out,” she remembered considering. “And I’m going to make clear it or I’m going to write down some extra or communicate or do one thing or, or—repair it.” However can she? Can anybody?
On the final day of the college 12 months in Oceanside, a well-to-do city on Lengthy Island, everybody was simply delighted to see Lucy Calkins. The younger Yale-educated principal of Fulton Avenue College 8, Frank Zangari, greeted her warmly, and on the finish of 1 lesson, a trainer requested for a selfie.
The teachings I noticed burdened the significance of self-expression and empathy with different viewpoints; a gaggle of sixth graders instructed me in regards to the books that they had learn that 12 months, which explored being poor in India and rising up Black in Sixties America. In each class, I watched Calkins communicate to youngsters with a combination of intense consideration and simple problem; she received down on the ground with a gaggle studying about orcas and frogs and peppered them with questions on how animals breathe. “May you discuss a minute in regards to the author’s craft?” she requested the sixth graders learning poetry. “Be extra particular. Give examples,” she instructed a fourth grader struggling to write down a memoir.
Together with her slim body, brown bob, and no-nonsense have an effect on, she jogged my memory of Nancy Pelosi. “I can’t retire; I don’t have any hobbies,” I overheard her saying to somebody later.
College 8 confirmed the strengths of Calkins’s strategy—which is presumably why she had advised we go to it collectively. But it surely additionally hinted on the downsides. For generations in American public training, there was a push and pull between two broad camps—one wherein academics are inspired to straight impart abilities and data, and a extra progressive one wherein youngsters are thought to be taught finest by firsthand expertise. On the subject of studying, the latter strategy dominates universities’ teaching programs and resonates with many academics; serving to youngsters see themselves as readers and writers feels extra emotionally satisfying than drilling them on diphthongs and trigraphs.
This pressure between the traditionalists and the progressives runs by a long time of wrangling over standardized exams and thru many of the main curricular controversies in latest reminiscence. Longtime educators tick off the assorted flash factors like Civil Struggle battlefields: outcome-based training, No Little one Left Behind, the Widespread Core. Each time, the pendulum went a method after which the opposite. “I began instructing elementary faculty in 1964,” says P. David Pearson, a former dean on the Berkeley College of Schooling, in California. “After which I went to grad faculty in, like, ’67, and there’s been a back-to-the-basics swing about each 10 years within the U.S., persistently.”
The progressives’ main perception is that classes targeted on repetitive instruction and simplified textual content extracts will be boring for college students and academics alike, and that many youngsters reply extra enthusiastically to discovering their very own pursuits. “We’re speaking about an strategy that treats youngsters as competent, mental that means makers, versus youngsters who simply have to be taught the code,” Maren Aukerman, a professor on the College of Calgary, instructed me. However opponents see that strategy as nebulous and undirected.
My time at College 8 was clearly meant to exhibit that Items of Research just isn’t hippie nonsense, however a rigorous curriculum that may succeed with the suitable academics. “There’s no query in my thoughts that the philosophy works, however with the intention to implement it, it takes a variety of work,” Phyllis Harrington, the district superintendent, instructed me.
College 8 is a cheerful faculty with nice outcomes. Nevertheless, whereas the college makes use of Calkins’s writing items for all grades, it makes use of her studying items solely from the third grade on. For first and second grades, the college makes use of Fundations, which is marketed as “a confirmed strategy to Structured Literacy that’s aligned with the science of studying.” In different phrases, it’s a phonics program.
Calkins’s upbringing was financially comfy however psychologically powerful. Each of her dad and mom had been medical doctors, and her father ultimately chaired the division of medication on the College at Buffalo. Calkins’s mom was “crucial, great individual in my life, however actually brutal,” she instructed me. If a mattress wasn’t made, her mom ripped off the sheets. If a coat wasn’t hung up, her mom dropped it into the basement. When the younger Lucy bit her fingernails, her mom tied dancing gloves onto her fingers. When she scratched the mosquito bites on her legs, her mom made her put on thick pantyhose on the peak of summer time.
The 9 Calkins youngsters raised sheep and chickens themselves. Her recollections of childhood are of horseback using within the chilly, countless hand-me-downs, and little tolerance for unhealthy conduct.
That’s the reason, Calkins instructed me, “nothing that Emily Hanford has stated grates on me greater than the rattling monogrammed towels.” However she is aware of that the cost of being privileged and out of contact has caught. Her pals had warned her about letting me into her dwelling in Dobbs Ferry, a reasonably suburb of New York, and I might see why. Her home is idyllic—on the finish of an extended personal drive, shaded by outdated bushes, with a grand piano within the hallway and a Maine-coon cat patrolling the wood flooring. Calkins has profited handsomely from textbook gross sales and coaching charges, and within the eyes of some individuals, that’s suspicious. (“Cash is the very last thing I ever take into consideration,” she instructed me.)
She turned eager about studying and writing as a result of she babysat for the kids of the literacy pioneer Donald Graves, whose philosophy will be summarized by one in all his most generally cited phrases: “Youngsters wish to write.” Even at a younger age, she believed in exhaustively ready enjoyable. “I might plan a bagful of issues I might deliver over there; I used to be one of the best babysitter you might ever have,” she stated. “We might do crafts tasks, and drama, you realize, and I might maintain the children busy all day.”
When Calkins was 14, Graves despatched her to be a counselor at a summer time camp in rural Maine. She remembers two youngsters specifically, Sophie and Charlie. Sophie was “so powerful and surly, and a sort of obese, insecure, powerful child,” however she opened up when Calkins took her horseback using after which requested her to write down about it. Charlie liked airplanes, and so she requested him to write down about these. The expertise cemented her lifelong perception that youngsters ought to learn and write as a type of self-expression.
After graduating from Williams School in 1973, she enrolled in a program in Connecticut that skilled academics to work in deprived districts. She learn every part about instructing strategies she might discover, and traveled to England, the place a progressive training revolution was in full swing.
Calkins returned to America decided to unfold this empowering philosophy. She earned a doctorate at NYU, and, in 1986, revealed a e book known as The Artwork of Instructing Writing. Later, she expanded her purview to studying instruction.
On the time, the zeitgeist favored an strategy often known as “entire language.” This advocated unbiased studying of full books and advised that youngsters ought to determine phrases from context clues quite than arduously sounding them out. Progressives liked it, as a result of it emphasised playfulness and company. However in observe, entire language had apparent flaws: Some youngsters do seem to select up studying simply, however many profit from targeted, direct instruction.
This strategy influenced Calkins as she developed her instructing philosophy. “Lucy Calkins sides, in most particulars, with the proponents of ‘entire language,’ ” The New York Occasions reported in 1997. Her heavyweight 2001 e book, The Artwork of Instructing Studying, has solely a single chapter on phonics in main grades; it does notice, nevertheless, that “researchers emphasize how necessary it’s for youngsters to develop phonemic consciousness in kindergarten.”
The writer Natalie Wexler has described Calkins’s ensuing strategy, balanced literacy, as an try and create a “peace treaty” within the studying wars: Phonics, sure, in case you should, but in addition writing workshops and unbiased studying with business youngsters’s books, quite than the stuffier grade-level decodable texts and accredited extracts. (Defenders of the previous technique argue that utilizing full books is extra cost-efficient, as a result of they are often purchased cheaply and utilized by a number of college students.) “If we make our youngsters imagine that studying has extra to do with matching letters and sounds than with creating relationships with characters like Babar, Madeline, Charlotte, and Ramona,” Calkins wrote, “we do extra hurt than good.”
Sentences like which are why critics noticed balanced literacy as a branding train designed to rehabilitate outdated strategies. “It was a strategic rebadging of entire language,” Pamela Snow, a cognitive-psychology professor at La Trobe College, in Australia, instructed me. Even lots of Calkins’s defenders concede that she was too gradual to embrace phonics because the proof for its effectiveness grew. “I believe she ought to have reacted earlier,” Pearson, the previous Berkeley dean, instructed me, however he added: “As soon as she modified, they had been nonetheless beating her for what she did eight years in the past, not what she was doing final month.”
For the primary a long time of her profession, Calkins was an influential thinker amongst progressive educators, writing books for academics. In 2003, although, Joel Klein, then the chancellor of the New York Metropolis public colleges, abruptly mandated her workshop strategy in nearly all the metropolis’s elementary colleges, alongside a separate, a lot smaller, phonics program. An article within the Occasions advised that some noticed Klein as “an unwitting captive of town’s liberal consensus,” however Klein brushed apart the criticisms of balanced literacy. “I don’t imagine curriculums are the important thing to training,” he stated. “I imagine academics are.” Now everyone within the metropolis’s public colleges can be “instructing Lucy.”
As different districts adopted New York’s lead, Items of Research turned one of the well-liked curricula in america. This led, inevitably, to backlash. A philosophy had grow to be a product—a particularly well-liked and financially profitable one. “As soon as upon a time there was a considerate educator who raised some attention-grabbing questions on how youngsters had been historically taught to learn and write, and proposed some revolutionary adjustments,” the writer Barbara Feinberg wrote in 2007. “However as she turned well-known, important debate largely ceased: her phrase turned regulation. Over time, a few of her strategies turned dogmatic and excessive, but her affect continued to develop.”
You wouldn’t realize it from listening to her fiercest detractors, however Calkins has, the truth is, repeatedly up to date Items of Research. In contrast to Irene Fountas and Homosexual Su Pinnell, who’ve stayed quiet throughout the newest furor and quietly reissued their curriculum with extra emphasis on phonics final 12 months, Calkins has even taken on her critics straight. In 2019—the 12 months after she added the devoted phonics texts to Items of Research—she revealed an eight-page doc known as “No One Will get to Personal the Time period ‘The Science of Studying,’ ” which referred dismissively to “phonics-centric individuals” and “the brand new hype about phonics.” This tone drove her opponents mad: Now that Calkins had been compelled to adapt, she needed to resolve what the science of studying was?
“Her doc just isn’t in regards to the science that I do know; it’s about Lucy Calkins,” wrote the cognitive neuroscientist Mark Seidenberg, one of many critics interviewed in Offered a Story. “The aim of the doc is to guard her model, her market share, and her standing amongst her many followers.”
Speaking with Calkins herself, it was onerous to nail all the way down to what extent she felt that the criticisms of her earlier work had been justified. After I requested her how she was desirous about phonics within the 2000s, she instructed me: “Each faculty has a phonics program. And I might at all times discuss in regards to the phonics packages.” She added that she introduced phonics specialists to Columbia’s Academics School a number of instances a 12 months to assist practice aspiring educators. (James Cunningham, at UNC Chapel Hill, backed this up, telling me, “She was definitely not sporting a sandwich billboard round: DON’T TEACH PHONICS.”)
However nonetheless, I requested Calkins, wouldn’t it be honest to say that phonics wasn’t your bag?
“I felt like phonics was one thing that you’ve the phonics specialists educate.”
So the place does this characterization of you being hostile towards phonics come from?
“Hopefully, you perceive I’m not silly. You would need to be silly to not educate a 5-year-old phonics.”
However some individuals didn’t, did they? They had been closely into context and cueing.
“I’ve by no means heard of a kindergarten trainer who doesn’t educate phonics,” Calkins replied.
As a result of that is America, the studying debate has grow to be a tradition struggle. When Offered a Story got here alongside in 2022, it resonated with a wide range of audiences, together with center-left training reformers and oldsters of youngsters with studying disabilities. But it surely additionally galvanized political conservatives. Calkins’s Items of Research was already below assault from the suitable: In 2021, an article within the Manhattan Institute’s Metropolis Journal titled “Items of Indoctrination” had criticized the curriculum, alleging that the way in which it teaches college students to investigate texts “quantities to little greater than radical proselytization by literature.”
The podcast was launched at an anxious time for American training. Throughout the coronavirus pandemic, many colleges—notably in blue states—had been closed for months at a time. Masking in lecture rooms made it tougher for youngsters to lip-read what their academics had been saying. Check scores fell, and have solely just lately begun to get better.
“Dad and mom had, for a time frame, a front-row seat based mostly on Zoom faculty,” Annie Ward, a just lately retired assistant superintendent in Mamaroneck, New York, instructed me. She questioned if that fueled a need for a “again to fundamentals” strategy. “If I’m a guardian, I wish to know the trainer is instructing and my child is sitting there soaking it up, and I don’t need this loosey-goosey” stuff.
Disgruntled dad and mom rapidly gathered on-line. Mothers for Liberty, a right-wing group that started off by opposing faculty closures and masks mandates, started lobbying state legislators to alter faculty curricula as nicely. The studying wars started to merge with different controversies, akin to how onerous colleges ought to push diversity-and-inclusion packages. (The Mothers for Liberty web site recommends Offered a Story on its assets web page.) “We’re failing youngsters on a regular basis, and Mothers for Liberty is asking it out,” a co-founder, Tiffany Justice, instructed Schooling Week in October of final 12 months. “The concept that there’s extra emphasis positioned on variety within the classroom, quite than instructing youngsters to learn, is alarming at finest. That’s felony.”
Ward’s district was not “instructing Lucy,” however utilizing its personal bespoke balanced-literacy curriculum. Within the aftermath of the pandemic, Ward instructed me, the district had a number of “contentious” conferences, together with one in January 2023 the place “we had ringers”—attendees who weren’t dad and mom or group members, however as an alternative appeared to be activists from exterior the district. “None of us within the room acknowledged these individuals.” That had by no means occurred earlier than.
I had met Ward at a dinner organized by Calkins at her dwelling, which can be the headquarters of Mossflower—the successor to the middle that Calkins used to guide at Academics School. The night demonstrated that Calkins nonetheless has star energy. On quick discover, she had managed to assemble half a dozen superintendents, assistant superintendents, and principals from New York districts.
“Any sort of disruption like this has you assume very fastidiously about what you’re doing,” Edgar McIntosh, an assistant superintendent in Scarsdale, instructed me. However he, like a number of others, was annoyed by the talk. Throughout his time as an elementary-school trainer, he had found that some youngsters might decode phrases—the fundamental ability developed by phonics—however struggled with their that means. He anxious that folks’ clamor for extra phonics may come on the expense of academics’ consideration to fluency and comprehension. Raymond Sanchez, the superintendent of Tarrytown’s faculty district, stated principals ought to be capable of clarify how they had been including extra phonics or decodable texts to current packages, quite than having “to throw every part out and discover a sequence that has a sticker that claims ‘science of studying’ on it.”
This, to me, is the important thing to the anti-Lucy puzzle. Hanford’s reporting was thorough and mandatory, however its conclusion—that entire language or balanced literacy would get replaced by a shifting, research-based motion—is tough to reconcile with how American training truly works. The science of studying began as a impartial description of a set of ideas, nevertheless it has now grow to be a model title, one other off-the-shelf resolution to America’s academic issues. The reply to these issues may not be to swap out one business curriculum package deal for one more—however that’s what the system is about as much as allow.
Gail Dahling-Hench, the assistant superintendent in Madison, Connecticut, has skilled this stress firsthand. Her district’s colleges don’t “educate Lucy” however as an alternative observe a bespoke native curriculum that, she says, makes use of classroom components related to balanced literacy, such because the workshop mannequin of scholars learning collectively in small teams, whereas additionally emphasizing phonics. That didn’t cease them from working afoul of the brand new science-of-reading legal guidelines.
In 2021, Connecticut handed a “Proper to Learn” regulation mandating that colleges select a Okay–3 curriculum from an accredited checklist of choices which are thought of compliant with the science of studying. Afterward, Dahling-Hench’s district was denied a waiver to maintain utilizing its personal curriculum. (Eighty-five districts and constitution colleges in Connecticut utilized for a waiver, however solely 17 had been profitable.) “I believe they received wrapped across the axle of considering that packages ship instruction, and never academics,” she instructed me.
Dahling-Hench stated the state gave her no helpful clarification for its determination—nor has it outlined the penalties for noncompliance. She has determined to stay with the bespoke curriculum, as a result of she thinks it’s working. In accordance with take a look at scores launched a couple of days after our dialog, her district is among the many best-performing within the state.
Holding the present curriculum additionally avoids the price of making ready academics and directors to make use of a brand new one—a transition that might be costly even for a tiny district like hers, with simply 5 colleges. “It will probably seem like $150,000 to $800,000 relying on which program you’re taking a look at, however that’s a onetime value,” Dahling-Hench stated. Then you’ll want to consider annual prices, akin to new workbooks.
You’ll be able to’t perceive this controversy with out appreciating the sums concerned. Refreshing a curriculum can value a state hundreds of thousands of {dollars}. Individuals on each side will due to this fact counsel that their opponents are motivated by cash—both saving their favored curriculum to maintain the earnings flowing, or getting wealthy by promoting faculty boards a wholly new one. Speaking with academics and researchers, I heard widespread frustration with America’s business strategy to literacy training. Politicians and bureaucrats have a tendency to like the thought of a packaged resolution—Purchase this and make all of your issues go away!—however the good curriculum doesn’t exist.
“Should you gave me any curriculum, I might discover methods to enhance it,” Aukerman, on the College of Calgary, instructed me. She thinks that when a instructing technique falls out of trend, its champions are sometimes personally vilified, no matter their good religion or experience. Within the case of Lucy Calkins and balanced literacy, Aukerman stated, “If it weren’t her, it could be another person.”

One apparent query in regards to the science of studying is, nicely … what’s it? The proof for some sort of specific phonics instruction is compelling, and states akin to Mississippi, which has adopted early screening to determine youngsters who battle to learn—and which holds again third graders if mandatory—seem like bettering their take a look at scores. Past that, although, issues get messy.
Dig into this topic, and you’ll find frontline academics and credentialed professors who contest each a part of the consensus. And I imply each half: Some teachers don’t even assume there’s a studying disaster in any respect.
American colleges could be ditching Items of Research, however balanced literacy nonetheless has its defenders. A 2022 evaluation in England, which mandates phonics, discovered that systematic opinions “don’t assist an artificial phonics orientation to the instructing of studying; they counsel {that a} balanced-instruction strategy is almost certainly to achieve success.”
The information on the results of particular strategies will be conflicting and complicated, which isn’t uncommon for training research, or psychological analysis extra usually. I really feel sorry for any well-intentioned superintendent or state legislator making an attempt to make sense of all of it. One of many lecture rooms at Oceanside College 8 had a wall show dedicated to “development mindset,” a modern intervention that encourages youngsters to imagine that as an alternative of their intelligence and skill being mounted, they’ll be taught and evolve. Hoping to enhance take a look at scores, many colleges have spent hundreds of {dollars} every implementing “development mindset” classes, which proponents as soon as argued must be a “nationwide training precedence.” (Some proponents additionally hoped, earnestly, that the strategy might assist deliver peace to the Center East.) However within the twenty years since development mindset first turned ubiquitous, the lofty claims made about its promise have come all the way down to earth.
Maintaining with all of that is greater than any trainer—greater than any faculty board, even—can moderately be anticipated to do. After I received in contact together with her, Emily Hanford despatched me seven emails with hyperlinks to research and background studying; I left Calkins’s home loaded down with items of her curricula for youthful college students. Extra adopted within the mail.
Even essentially the most modest pronouncements about what’s occurring in American colleges are tough to confirm, due to the sheer variety of districts, academics, and pupils concerned. In Offered a Story, Hanford advised that some colleges had been succeeding with Items of Research solely as a result of dad and mom employed private tutors for his or her youngsters. However corroborating this with information is unattainable. “I haven’t found out a technique to quantify it, besides in a really sturdy anecdotal manner,” Hanford instructed me.
Some academics love “instructing Lucy,” and others hate it. Is one group delusional? And in that case, which one? Jenna and Christina, who’ve each taught kindergarten in New York utilizing Items of Research, instructed me that the curriculum was too invested within the concept of youngsters as “readers” and “writers” with out giving them the fundamental abilities wanted to learn and write. (They requested to be recognized solely by their first names in case {of professional} reprisals.) “It’s a chunk of shit,” Christina stated. She added: “We’re anticipating them to use abilities that we haven’t taught them and that they aren’t coming to highschool with. I’ve been making an attempt to specific that there’s an issue and I get known as damaging.” Jenna had resorted to a covert technique, secretly instructing phonics for as much as 90 minutes a day as an alternative of the temporary classes she was instructed to offer.
However for each Jenna or Christina, there’s a Latasha Holt. After a decade as a third- and fourth-grade trainer in Arkansas, Holt is now an affiliate professor of elementary literacy on the College of Louisiana at Lafayette, the place she has watched from the sidelines because the tide turned towards Calkins. “The dismantling of this factor, it received to me, as a result of I had taught below Items of Research,” she instructed me. “I’ve used it, and I knew how good it was. I had lived it; I’ve seen it work; I knew it was good for teenagers.”
Aubrey Kinat is a third-grade trainer in Texas who just lately left her place at a public faculty as a result of it determined to drop Items of Research. (The varsity now makes use of one other curriculum, which was deemed to align higher with the science of studying.) Out of the blue, she was pushed away from full novels and towards accredited excerpts, and her classes turned way more closely scripted. “I felt like I used to be speaking a lot,” she instructed me. “It took the enjoyment out of it.”
For a lot of faculty boards going through newly politicized dad and mom who got here out of the pandemic with sturdy opinions, ditching Lucy has had the glad aspect impact of giving adults way more management over what youngsters learn. Calkins and a few of her dinner visitors had advised that this could be the true motive for the animus round unbiased studying. “I do begin to marvel if this actually is about wanting to maneuver everyone in direction of textbooks,” Calkins stated.
Eighteen months after her sequence launched, Hanford returned in April 2024 with two follow-up episodes of Offered a Story, which took a much less polemical tone. Unsurprisingly so: Calkins had misplaced, and she or he had gained.
The science of studying is the brand new consensus in training, and its advocates are the brand new institution. It’s now on the hook for the curriculum adjustments that it prompted—and for America’s studying efficiency extra usually. That’s an uncomfortable place for individuals who care extra about analysis than about successful political fights.
Among the neuroscience underpinning Offered a Story was supplied by Seidenberg, a professor emeritus on the College of Wisconsin at Madison. (He didn’t reply to an interview request.) Because the sequence aired, he has welcomed the transfer away from Items of Research, however he has additionally warned that “not one of the different main business curricula which are at present obtainable had been based mostly on the related science from the bottom up.”
As a result of the usefulness of phonics is likely one of the few science-of-reading conclusions that’s instantly understandable to laypeople, “phonics” has come to face in for the entire philosophy. In a weblog publish final 12 months, Seidenberg lamented that, on a latest Zoom name, a trainer had requested in the event that they wanted to maintain instructing phonemic consciousness as soon as youngsters had been good readers. (The reply is not any: Sounding out letters is what you do till the method turns into computerized.) Seidenberg now anxious that the science of studying is “susceptible to turning into a brand new pedagogical dogma.”
Hanford has additionally expressed ambivalence in regards to the results of Offered a Story. She in contrast the state of affairs to the aftermath of No Little one Left Behind, a George W. Bush–period federal training initiative that closely promoted a literacy program known as Studying First. “It turned targeted on merchandise and packages,” Hanford instructed me, including that the ethos was “eliminate entire language and purchase one thing else.” Nevertheless, she is glad that the significance of phonics—and the analysis backing it—is now extra extensively understood, as a result of she thinks this may break the cycle of revolution and counterrevolution. She added that each time she talks with lawmakers, she stresses the significance of constant to hearken to academics.
What about her portrait of Calkins as wealthy, privileged, oblivious? Overlook the monogrammed towels, I instructed Hanford; there’s a extra benign clarification for Calkins’s worldview: In all places she goes, she meets individuals, just like the academics and youngsters in Oceanside, who’re overjoyed to see her, and eager to inform her how a lot they love Items of Research.
However Hanford instructed me that she’d included the towels line as a result of “the overwhelming majority of academics, particularly elementary-school academics, in America are white, middle-class girls.” Many of those girls, she thought, had loved faculty themselves and didn’t intuitively know what it was wish to battle with studying to learn and write.
Reporting this story, I used to be reminded many times that training is each a mass phenomenon and a deeply private one. Individuals I spoke with would say issues like Effectively, he’s by no means performed any classroom analysis. She’s by no means been a trainer. They don’t perceive issues the way in which I do. The training professors would complain that the cognitive scientists didn’t perceive the historical past of the studying wars, whereas the scientists would complain that the training professors didn’t perceive the newest peer-reviewed analysis. In the meantime, a trainer should command a category that features college students with dyslexia in addition to those that discover studying a breeze, and children whose dad and mom learn to them each night time alongside youngsters who don’t communicate English at dwelling. On the identical time, faculty boards and state legislators, confronted with indignant dad and mom and a welter of conflicting testimony, should reply a easy query: Ought to we be “instructing Lucy,” or not?
Regardless of how painful the previous few years have been, although, Calkins is decided to maintain preventing for her legacy. At 72, she has each the vitality to begin over once more at Mossflower and the pragmatism to have promised her property to additional the trigger as soon as she’s gone. She nonetheless has a “ferocious” drive, she instructed me, and a deep conviction in her strategies, whilst they evolve. She doesn’t need “to faux it’s a brand-new strategy,” she stated, “when the truth is we’ve simply been studying; we’re simply incorporating extra issues that we’ve realized.”
However now that balanced literacy is as retro as entire language, Calkins is making an attempt to give you a brand new title for her program. She thought she may attempt “complete literacy”—or perhaps “rebalancing literacy.” No matter it takes for America to as soon as once more really feel assured about “instructing Lucy.”
This text seems within the December 2024 print version with the headline “Instructing Lucy.” Once you purchase a e book utilizing a hyperlink on this web page, we obtain a fee. Thanks for supporting The Atlantic.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Byr_DI_Bside_Social-a424baa294aa4744b356bea5aca5b00c.jpg)